Introduction
Masscan is the next tool on our list that can be used to scan for IPv6 addresses for open ports and to discover services running on them. Because of a custom ad hoc TCP/IP stack, it is recommended to set source IP address and the port number to prevent interference from the local operating system stack, when performing complex scans. Like nmap, masscan allows you to set source IP and port addresses using command line arguments.
Masscan is an extremely fast port scanner capable of scanning both IPv4 and IPv6 addresses. It finds its usage mostly in research projects to map services around the Internet and given how fast it can scan hosts, it can honestly be an overkill to scan a few hosts with masscan :)
Masscan is also capable of some level of “service detection” as it can also complete an initiated TCP connection and interact with the app/service at that port in order to grab simple “banner” information. This requires prepping the system so that masscan can intercept the responses instead of the host system’s networking stack. For additional details to do proper banner grabbing, take a look at the documentation at https://github.com/robertdavidgraham/masscan#banner-checking
Masscan supports banner checking on the following protocols:
- FTP
- HTTP
- IMAP4
- memcached
- POP3
- SMTP
- SSH
- SSL
- SMBv1
- SMBv2
- Telnet
- RDP
- VNC
Note: As is with any security software, make sure that the scans are conducted on the networks where you are allowed to do so with appropriate permissions.
Before we begin
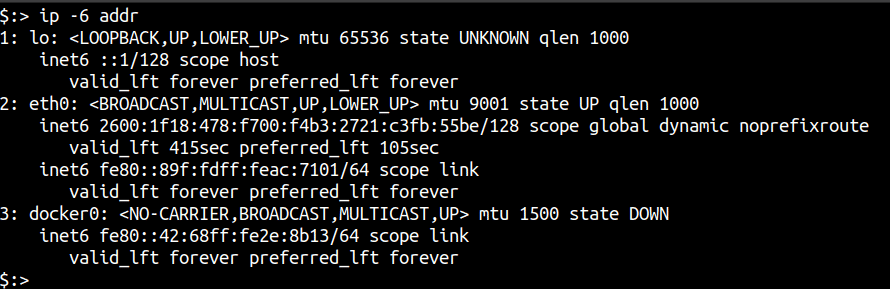
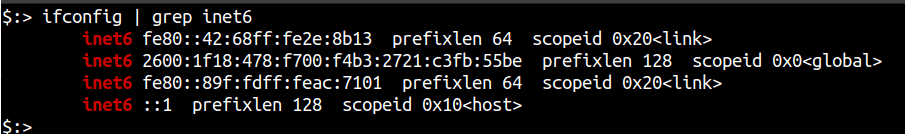
Like any other IPv6 scanning tool, your system needs to support IPv6 in order to utilise Masscan’s scanning capabilities. To verify that your system and network are properly configured to have IPv6 access, you can run either of the following commands:
-
ip -6 addr
-
ifconfig | grep inet6
Setting up Masscan
Masscan runs with no issues on most Linux systems. On Debian/Ubuntu, you can simply clone the repo and build the binary using a C compiler like gcc.
sudo apt-get --assume-yes install git make gcc
git clone https://github.com/robertdavidgraham/masscan
cd masscan
make
make install
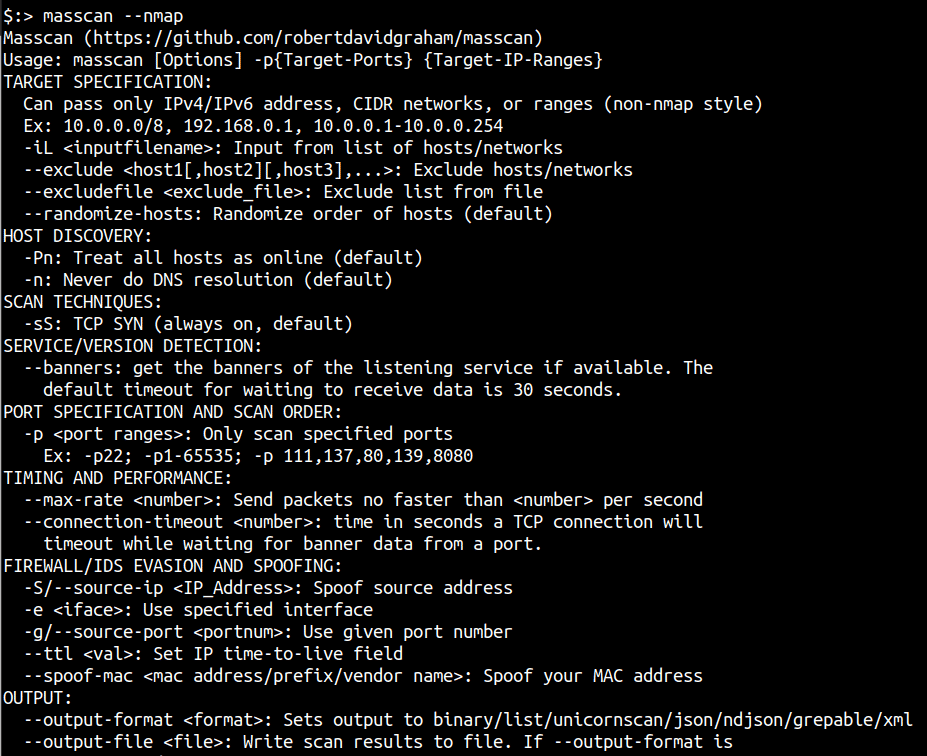
A very cool help feature of masscan is the nmap style help menu it has. Simply invoke masscan --nmap to see the options that masscan supports which have been signed with nmap arguments to ensure familiarity.
Scanning IPv6 with Masscan
Scanning IPv6 addresses is similar to using nmap. For example, the following command will scan the IPv6 address subnet for ports 80 and 8000 to 8100.
masscan -p80,8000-8100 2603:3001:2d00:da00::/112
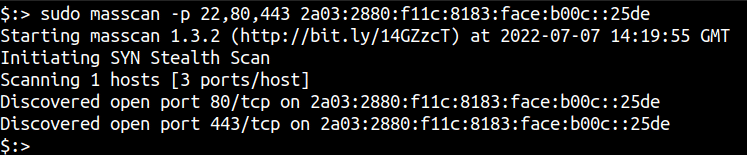
As mentioned earlier, although the program works for smaller networks it is actually designed for scanning really large networks, like the entire Internet.
Scanning the entire IPv6 address space is inadvisable as this will generate a lot of traffic and even if you kill the program, the packets would have already left your system.
The documentation also recommends not to scan the Internet without using an exclude list.
"Scanning the entire Internet is bad. For one thing, parts of the Internet react badly to being scanned. For another thing, some sites track scans and add you to a ban list, which will get you firewalled from useful parts of the Internet. Therefore, you want to exclude a lot of ranges."
To blacklist or exclude ranges, you can use the following syntax where exclude.txt contains a list of IP ranges to avoid:
masscan ::/0 -p0-65535 --excludefile exclude.txt
Conclusion
In this article we looked at masscan, which is one of the fastest port scanning tools available that comes with its own TCP/IP stack. Masscan is really easy to build and run and since it is written in C, it’s not clunky like other tools that we have seen.
This article is part of a series on scanning IPv6 addresses. Come back for our next article in the series in which we will take a look at the last IPv6 scanner in our list - v6disc.
Riyaz Walikar
Founder & Chief of R&D
Riyaz is the founder and Chief of R&D at Kloudle, where he hunts for cloud misconfigurations so developers don’t have to. With over 15 years of experience breaking into systems, he’s led offensive security at PwC and product security across APAC for Citrix. Riyaz created the Kubernetes security testing methodology at Appsecco, blending frameworks like MITRE ATT&CK, OWASP, and PTES. He’s passionate about teaching people how to hack—and how to stay secure.

Riyaz Walikar
Founder & Chief of R&D
Riyaz is the founder and Chief of R&D at Kloudle, where he hunts for cloud misconfigurations so developers don’t have to. With over 15 years of experience breaking into systems, he’s led offensive security at PwC and product security across APAC for Citrix. Riyaz created the Kubernetes security testing methodology at Appsecco, blending frameworks like MITRE ATT&CK, OWASP, and PTES. He’s passionate about teaching people how to hack—and how to stay secure.